Reporting Analytics vs. Financial Reporting: Is There a Difference?
Jet Global
OCTOBER 26, 2021
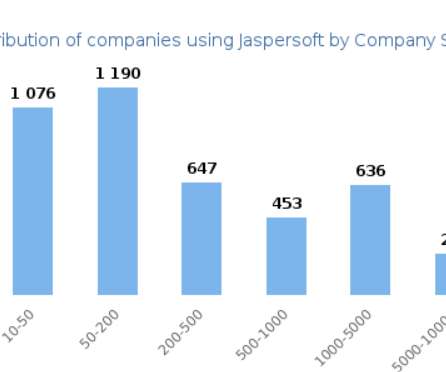
The terms “reporting” and “analytics” are often used interchangeably. In fact there are some very important differences between the two, and understanding those distinctions can go a long way toward helping your organization make best use of both financial reporting and analytics. Financial Reporting.






















Let's personalize your content